Docker Model Runner Tutorial and Cheatsheet: Mac, Windows and Linux Support
Whether you're building generative AI applications, experimenting with machine learning workflows, or integrating AI into your software development lifecycle, Docker Model Runner provides a consistent, secure, and efficient way to work with AI models locally.

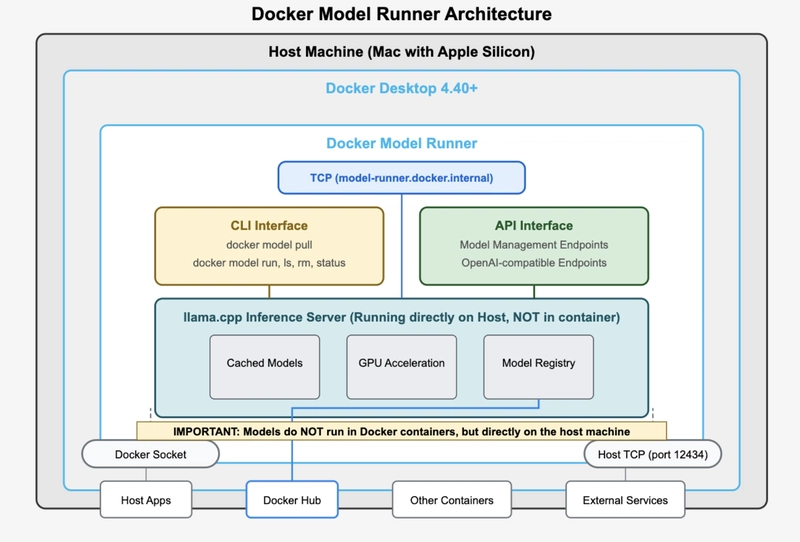
Docker Model Runner is a feature that allows you to run and interact with AI models directly from the command line or through the Docker Desktop GUI. It's rightly integrated into Docker Desktop and enables you to pull models from Docker Hub, run them locally, and interact with them using OpenAI-compatible APIs.

What can you do with Docker Model Runner?
With Docker Model Runner, you can:
- Pull and run AI models locally: Download models from Docker Hub and any OCI-compliant registry so that you can run these models on your machine.
Docker Model Runner streamlines the process of pulling, running, and serving large language models (LLMs) and other AI models directly from Docker Hub or any OCI-compliant registry.
- Interact with models via CLI or GUI: Use the command line or Docker Desktop’s Models tab to run models and interact with them in chat mode or by submitting prompts.
- Use OpenAI-compatible APIs: Interact with models using standard OpenAI API endpoints, making integration with existing AI applications straightforward.
- Package and publish models: Package GGUF files as OCI Artifacts and publish them to any container registry, including Docker Hub.
- Integrate with Docker Compose and Testcontainers: Run AI models as part of multi-container applications or automated test environments.
- Manage and view logs: List, inspect, and view logs for your local models to help with troubleshooting and monitoring.
With Docker Model Runner, the AI model DOES NOT run in a container. Instead, Docker Model Runner uses a host-installed inference server (llama.cpp for now) that runs natively on your Mac rather than containerizing the model.
Models are cached locally after the first use for faster access, and are loaded into memory only when needed to optimize resource usage.
Platform Support
| Platform | Status | GPU Support | Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| macOS (Apple Silicon) | ✅ Full | Metal | 4.40+ |
| Windows | ✅ Full | NVIDIA CUDA | 4.41+ |
| Linux (Docker CE) | ✅ Full | NVIDIA | Latest |
Here's more details:
- Status: ✅ Fully Supported (Since Docker Desktop 4.40)
- Requirements:
- macOS with Apple Silicon (M1, M2, M3, M4)
- Docker Desktop 4.40 or later
- 8GB+ RAM recommended
- GPU Support: Native Metal acceleration via host-based execution
Windows
- Status: ✅ Supported (Since Docker Desktop 4.41)
- Requirements:
- Windows 10/11 (x64 or ARM64)
- Docker Desktop 4.41 or later
- For GPU: NVIDIA GPU with compatible drivers
- 8GB+ RAM recommended
- GPU Support: NVIDIA CUDA acceleration (optional, requires additional setup)
Linux
- Status: ✅ Supported (Docker CE/Community Edition)
- Requirements:
- Linux distribution with Docker Engine
- Docker CE (Community Edition)
- 8GB+ RAM recommended
- For GPU: NVIDIA GPU with Container Toolkit
- Note: The status quo is Docker Model Runner support in Docker Desktop on macOS and Windows and support for Docker CE on Linux (including WSL2)
💡Does Model Runner uses GPU?
Docker Model Runner can use GPU acceleration. On Windows, GPU-backed inference is supported if you have an NVIDIA GPU and enable the relevant setting in Docker Desktop. When you enable Docker Model Runner in Docker Desktop, you will see an option to enable GPU-backed inference if your hardware supports it.
Docker Desktop runs llama.cpp directly on your host machine. This allows direct access to the hardware GPU acceleration on Apple Silicon.
Let's look at how to get started with Docker Model Runner on the Windows platform.
Using Docker Model Runner on Windows x86 system
- Install the latest version of Docker Desktop(4.42+)
- Ensure that “Docker Model Runner” is enabled.
- X86 System with Windows 11 Pro
- Enable Docker Model Runner under Settings
The "Enable host-side TCP support" feature allows Docker Model Runner to additionally accept connections on the host OS on the specified TCP port (default: 12434) rather than only through the host Docker socket (/var/run/docker.sock). You can change this to another port if needed, particularly if 12434 is already in use by another application. We will see its usage later in the docs.
- Click “Docker Hub” and search for your preferred AI Model.
- Select the model and start chatting with the AI model by adding your prompt
There are two ways to enable Model Runner - either using CLI or using Docker Dashboard. You already saw how to use Model Runner using Docker Dashboard.
Let's look at how to get started with Model Runner using Powershell:
Using PowerShell
If you want to enable Model Runner using CLI, here's a quick way:
Enabling the Model Runner
docker desktop enable model-runner
Run the following command to see the usage of Model Runner CLI:
docker model --help
Usage: docker model COMMAND
Docker Model Runner
Commands:
inspect Display detailed information on one model
list List the available models that can be run with the Docker Model Runner
pull Download a model
rm Remove a model downloaded from Docker Hub
run Run a model with the Docker Model Runner
status Check if the Docker Model Runner is running
version Show the Docker Model Runner version
Run 'docker model COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
Check if the Model Runner is running or not
docker model status
Docker Model Runner is running
List the available models
docker model ls
MODEL PARAMETERS QUANTIZATION ARCHITECTURE FORMAT MODEL ID CREATED SIZE
The response shows an empty list.
Let’s go ahead and download the model from the Docker Hub.
Download a model
docker model pull ai/llama3.2:1B-Q8_0
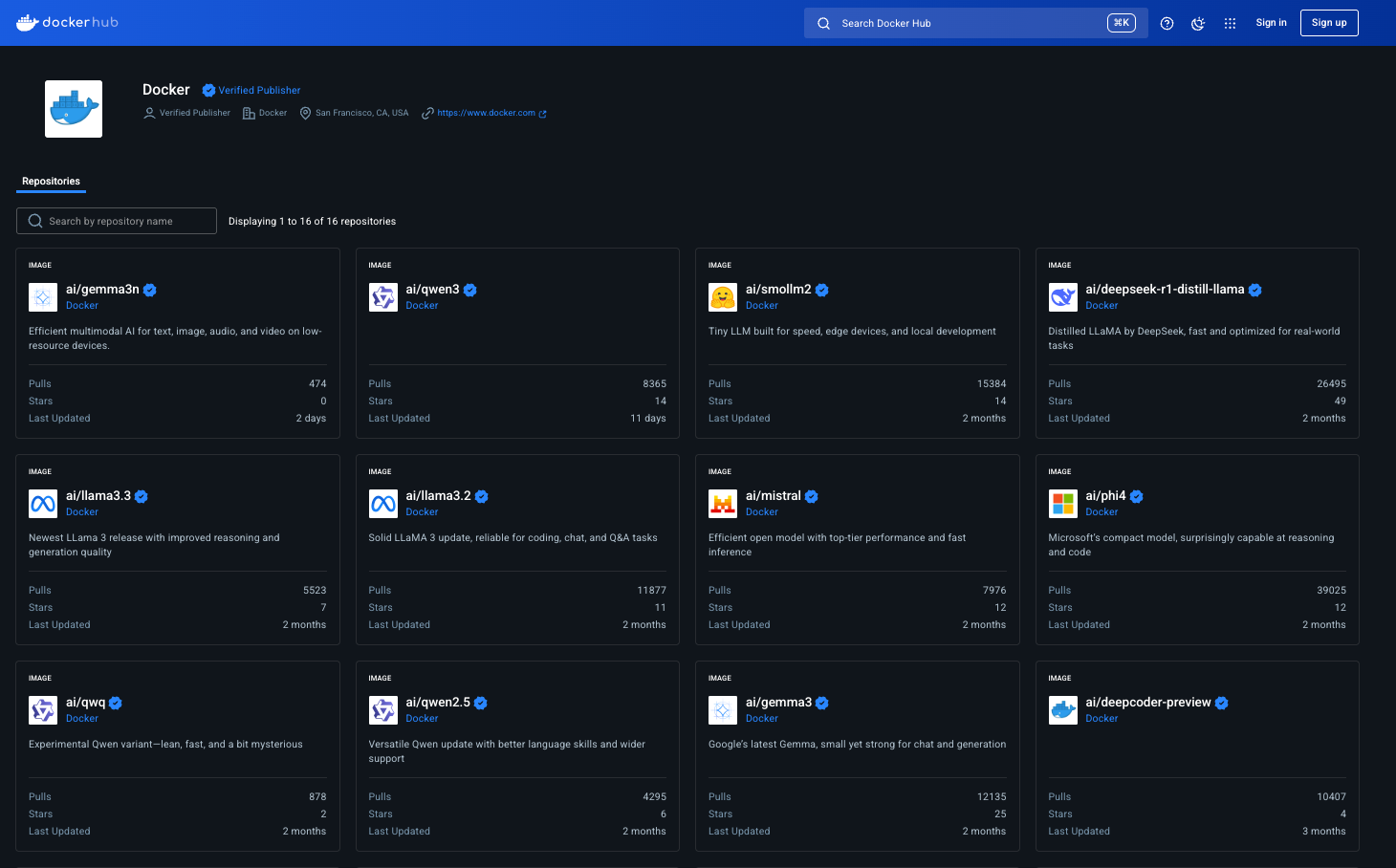
All these models are hosted on https://hub.docker.com/u/ai:
- ai/gemma3
- ai/llama3.2
- ai/qwq
- ai/mistral-nemo
- ai/mistral
- ai/phi4
- ai/qwen2.5
- ai/deepseek-r1-distill-llama (distill means it’s not the actual RL-ed deepseek, it’s a llama trained on DeepSeek-R1 inputs/outputs)
- and many more
List the Model
docker model ls
MODEL PARAMETERS QUANTIZATION ARCHITECTURE MODEL ID CREATED SIZE
ai/llama3.2:1B-Q8_0 1.24 B Q8_0 llama a15c3117eeeb 20 hours ago 1.22 GiB
Use the following command to send a single message:
docker model run ai/llama3.2:1B-Q8_0 "Hi"
Hello! How can I help you today?
Run the Model in interactive mode
docker model run ai/llama3.2:1B-Q8_0
Interactive chat mode started. Type '/bye' to exit.
> why is water blue?
Water appears blue because ...
Remove the model
docker model rm ai/llama3.2:1B-Q8_0
All the above listed commands and steps works for MacOS too.
💡Important Note:
Models are stored as OCI artifacts in Docker Hub, which means the standardized format will be supported by any other Docker Registries. So it will also work if you use your company's internal artifact registries.
Working with models as OCI artifacts has a number of advantages over the traditional approach of packaging an AI runtime and the model in a Docker image for a container. For example, you get no compression of the layers which is very good because model weights are largely uncompressible. So you get faster deployments, and lower disk requirements because you don't need to have both the compressed and uncompressed versions of the model weights on your disk improving UX a lot.
Using Docker Model Runner on Linux (Ubuntu, Red Hat, Fedora)
Prerequisites
- Linux system (Ubuntu/Debian recommended)
- Docker Engine installed
- At least 4GB RAM
- Internet connection for downloading models
Let's get started!
Step 1: Install Docker Model Runner
First, update your system and install the Docker Model Runner plugin:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-model-plugin
If you're using Fedora or Red Hat, run the following commands:
sudo dnf update
sudo dnf install docker-model-plugin
Step 2: Verify Installation
Check that Docker Model Runner is properly installed:
docker model version
You should see version information for Docker Model Runner. The docker model command is now available alongside your regular Docker commands.
Step 3: Run Your First AI Model
Now let's deploy an AI model using Docker Model Runner:
docker model run ai/smollm2
This command will:
- Pull the SmolLM2 model (270 MB in size, 360 million parameters) from Docker Hub
- Perfect for Chat assistants, Text-extraction, Rewriting and summarization tasks.
- Start a model server
- Make the model available via API on port 12434
Start chatting with the model. Once done, you can exit by typing /bye.
Let's verify the model is running:
docker model ps
Supported Model Format
Docker Model Runner supports models in the GGUF (GPT-style General Use Format), a lightweight binary file format designed for efficient local inference. This format includes model weights, tokenizer, and metadata, making it ideal for packaging and distributing LLMs in containerized environments.
You can also directly package a model file in GGUF format as an OCI Artifact and publish it to Docker Hub.
# Download a model file in GGUF format, e.g. from HuggingFace
$ curl -L -o model.gguf https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Mistral-7B-v0.1-GGUF/resolve/main/mistral-7b-v0.1.Q4_K_M.gguf
# Package it as OCI Artifact and push it to Docker Hub
$ docker model package --gguf "$(pwd)/model.gguf" --push myorg/mistral-7b-v0.1:Q4_K_M
Does Model Runner work with Docker Compose?
That's a great question.
Yes, Docker Model Runner works with Docker Compose. Starting from Docker Compose v2.35.0 and Docker Desktop 4.41, you can integrate Model Runner into your Compose applications.
Compose introduces a new service type called provider, which allows you to declare model dependencies using the model type. This lets you define and run AI-powered applications alongside your other services in a multi-container setup. During docker compose up, Model Runner automatically pulls and runs the specified model, and passes connection details to dependent services via environment variables.
For example, you can declare a model provider service in your docker-compose.yml.
Here's a demo project called aiwatch - AI Model Management and Observability powered by Docker Model Runner. This project showcases a complete Generative AI interface that includes:
- React/TypeScript frontend with a responsive chat UI
- Go backend server for API handling
- Integration with Docker's Model Runner to run Llama 3.2 locally
- Comprehensive observability with metrics, logging, and tracing
- llama.cpp metrics integration directly in the UI

services:
backend:
env_file: 'backend.env'
build:
context: .
target: backend
ports:
- '8080:8080'
- '9090:9090' # Metrics port
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock # Add Docker socket access
healthcheck:
test: ['CMD', 'wget', '-qO-', 'http://localhost:8080/health']
interval: 3s
timeout: 3s
retries: 3
networks:
- app-network
depends_on:
- llm
frontend:
build:
context: ./frontend
ports:
- '3000:3000'
depends_on:
backend:
condition: service_healthy
networks:
- app-network
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:v2.45.0
volumes:
- ./prometheus/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
command:
- '--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml'
- '--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus'
- '--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries'
- '--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles'
- '--web.enable-lifecycle'
ports:
- '9091:9090'
networks:
- app-network
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:10.1.0
volumes:
- ./grafana/provisioning:/etc/grafana/provisioning
- grafana-data:/var/lib/grafana
environment:
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin
- GF_USERS_ALLOW_SIGN_UP=false
- GF_SERVER_DOMAIN=localhost
ports:
- '3001:3000'
depends_on:
- prometheus
networks:
- app-network
jaeger:
image: jaegertracing/all-in-one:1.46
environment:
- COLLECTOR_ZIPKIN_HOST_PORT=:9411
ports:
- '16686:16686' # UI
- '4317:4317' # OTLP gRPC
- '4318:4318' # OTLP HTTP
networks:
- app-network
# New LLM service using Docker Compose's model provider
llm:
provider:
type: model
options:
model: ${LLM_MODEL_NAME:-ai/llama3.2:1B-Q8_0}
volumes:
grafana-data:
networks:
app-network:
driver: bridgeAPI Access
- From Host (HTTP)
# Enable TCP access (if not done during setup)
docker desktop enable model-runner --tcp 12434
# Make API calls
curl http://localhost:12434/engines/llama.cpp/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "ai/smollm2",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello! How are you?"}
]
}'- From Containers
# Models accessible via special DNS name
curl http://model-runner.docker.internal/engines/llama.cpp/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "ai/smollm2",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the capital of France?"}
]
}'- Via Docker Socket (Unix)
curl --unix-socket /var/run/docker.sock \
localhost/exp/vDD4.40/engines/llama.cpp/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "ai/smollm2",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "Tell me a joke"}
]
}'📋 Core Commands
Model Management
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
docker model pull <model> | Download model from Docker Hub | docker model pull ai/smollm2 |
docker model list | List local models | docker model list |
docker model rm <model> | Remove local model | docker model rm ai/smollm2 |
docker model status | Check Model Runner status | docker model status |
docker model inspect <model> | Show model details | docker model inspect ai/smollm2 |
docker model df | Show disk usage | docker model df |
Model Execution
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
docker model run <model> "<prompt>" | One-time prompt | docker model run ai/smollm2 "Hello" |
docker model run <model> | Interactive chat mode | docker model run ai/smollm2 |
docker model run -it <model> | Interactive mode (explicit) | docker model run -it ai/smollm2 |
Model Publishing
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
docker model push <namespace>/<model> | Push model to registry | docker model push myorg/my-model |
docker model tag <source> <target> | Tag model | docker model tag ai/smollm2 my-model:latest |
docker model package <gguf-file> | Package GGUF as OCI artifact | docker model package model.gguf |
Debugging & Monitoring
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
docker model logs | View logs | docker model logs |
docker model logs -f | Follow logs in real-time | docker model logs -f |
docker model logs --no-engines | Exclude engine logs | docker model logs --no-engines |
Runner Management (Docker CE)
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
docker model install-runner | Install runner explicitly | docker model install-runner |
docker model uninstall-runner | Remove runner | docker model uninstall-runner |
🌐 API Endpoints
Base URLs
| Access Method | URL | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| From containers | http://model-runner.docker.internal/ | Special DNS name |
| From host (TCP) | http://localhost:12434/ | Requires TCP enabled |
| From host (Unix) | Unix socket: /var/run/docker.sock | Prefix paths with /exp/vDD4.40 |
Docker Model Management APIs
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
POST | /models/create | Create/pull model |
GET | /models | List models |
GET | /models/{namespace}/{name} | Get model info |
DELETE | /models/{namespace}/{name} | Delete model |
OpenAI-Compatible APIs
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
GET | /engines/llama.cpp/v1/models | List available models |
GET | /engines/llama.cpp/v1/models/{namespace}/{name} | Get specific model |
POST | /engines/llama.cpp/v1/chat/completions | Chat completions |
POST | /engines/llama.cpp/v1/completions | Text completions |
POST | /engines/llama.cpp/v1/embeddings | Generate embeddings |
💡 Tip: You can omitllama.cppfrom paths:/engines/v1/chat/completions
Further Readings: